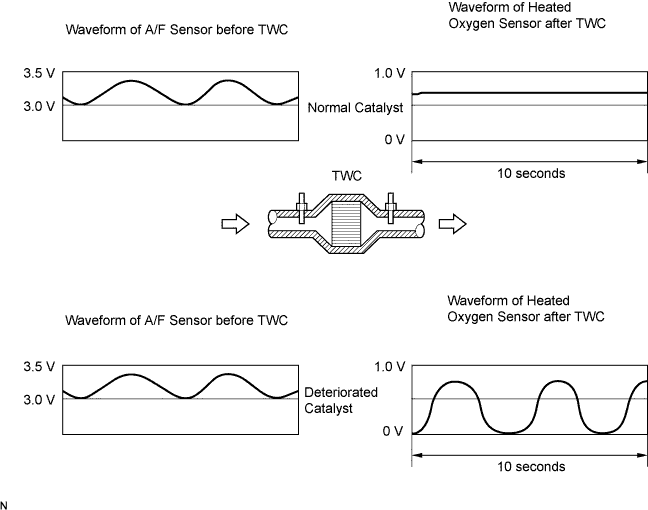
DTC P0420 Catalyst System Efficiency Below Threshold (Bank 1) |
| DTC No. | DTC Detection Condition | Trouble Area |
| P0420 | After engine and catalyst are warmed up, and while vehicle is driven within set vehicle speed and engine speed range: Waveform of heated oxygen sensor frequently fluctuates between rich and lean (2 trip detection logic) |
|
| Tester Display (Sensor) | Injection Volume | Status | Voltage |
| AFS B1 S1 (A/F) | +25% | Rich | Less than 3.0 V |
| AFS B1 S1 (A/F) | -12.5% | Lean | More than 3.35 V |
| O2S B1 S2 (HO2) | +25% | Rich | More than 0.55 V |
| O2S B1 S2 (HO2) | -12.5% | Lean | Less than 0.4 V |
| Case | A/F Sensor (Sensor 1) Output Voltage | HO2 Sensor (Sensor 2) Output Voltage | Main Suspected Trouble Area | ||
| 1 | Injection Volume +25% -12.5% |  | Injection Volume +25% -12.5% |  | - |
| Output Voltage More than 3.35 V Less than 3.0 V | 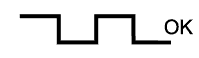 | Output Voltage More than 0.55 V Less than 0.4 V |  | ||
| 2 | Injection Volume +25% -12.5% | 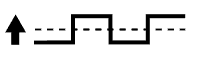 | Injection Volume +25% -12.5% | 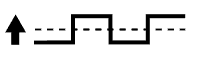 |
|
| Output Voltage Almost no reaction |  | Output Voltage More than 0.55 V Less than 0.4 V |  | ||
| 3 | Injection Volume +25% -12.5% | 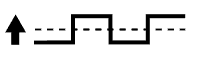 | Injection Volume +25% -12.5% | 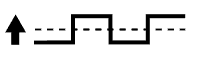 |
|
| Output Voltage More than 3.35 V Less than 3.0 V |  | Output Voltage Almost no reaction |  | ||
| 4 | Injection volume +25% -12.5% | 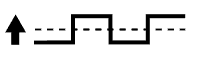 | Injection Volume +25% -12.5% | 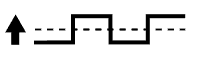 |
|
| Output Voltage Almost no reaction |  | Output Voltage Almost no reaction |  | ||
| 1.CHECK OTHER DTCS OUTPUT (IN ADDITION TO DTC P0420) |
Connect the intelligent tester to the DLC3.
Turn the ignition switch ON and turn the intelligent tester ON.
Select the following menu items: Powertrain / Engine and ECT / DTC.
Read DTCs.
| Display (DTC output) | Proceed to |
| P0420 | A |
| P0420 and other DTCs | B |
|
| ||||
| A | |
| 2.PERFORM ACTIVE TEST (A/F CONTROL) |
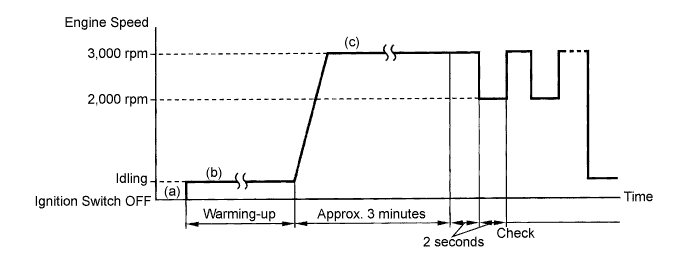
Connect the intelligent tester to the DLC3.
Start the engine and turn the tester ON.
Warm up the engine at an engine speed of 2,500 rpm for approximately 90 seconds.
On the tester, select the following menu items: Powertrain / Engine and ECT / Active Test / A/F Control.
Perform the A/F Control operation with the engine in an idling condition (press the right or left button to change the fuel injection volume.)
Monitor the output voltages of the A/F and HO2 sensors (AFS B1 S1 and O2S B1 S2 or AFS B2S1 and O2S B2S2) displayed on the tester.
| Tester Display (Sensor) | Injection Volume | Status | Voltage |
| AFS B1 S1 (A/F) | +25% | Rich | Less than 3.0 V |
| AFS B1 S1 (A/F) | -12.5% | Lean | More than 3.35 V |
| O2S B1 S2 (HO2) | +25% | Rich | More than 0.55 V |
| O2S B1 S2 (HO2) | -12.5% | Lean | Less than 0.4 V |
| Status AFS B1 S1 | Status O2S B1 S2 | A/F Condition and A/F and HO2 Sensor Condition | Misfire | Main Suspected Trouble Areas | Proceed to |
| Lean/Rich | Lean/Rich | Normal | - |
| A |
| Lean | Lean/Rich | A/F sensor malfunction | - |
| B |
| Rich | Lean/Rich | A/F sensor malfunction | - |
| B |
| Lean/Rich | Lean | HO2 sensor malfunction | - |
| C |
| Lean/Rich | Rich | HO2 sensor malfunction | - |
| C |
| Lean | Lean | Actual air-fuel ratio lean | May occur |
| A |
| Rich | Rich | Actual air-fuel ratio lean | - |
| A |
|
| ||||
|
| ||||
| A | |
| 3.CHECK FOR EXHAUST GAS LEAKAGE |
|
| ||||
| OK | ||
| ||