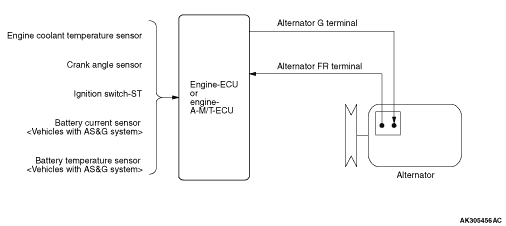
|
|
The engine-ECU restricts the power generation when all of the following conditions are
satisfied.
|
|
|
- During the vehicle running (except the speed reduction)
- The electrical accessory loads are small.
- After the engine starts, the battery temperature is 0°C or more.
- The amount of battery discharge is less than the specified value.
- The vehicle is not in the forcible full charge mode.
- The battery deterioration judgement decides that the battery is not deteriorated.
|
|
|
The engine-ECU is in the forcible full charge mode when the following start conditions
are satisfied. During the mode, the alternator always generates the electrical power of approximately
14.4 V. When detecting that the battery is fully charged, the engine-ECU cancels the forcible
full charge mode.
|
|
|
- When the battery terminal is disconnected.
- After the specified time has passed since the previous judgment on the completed
full charge
- The amount of battery discharge is more than the specified value.
- When the battery deterioration judgement decides that the battery is deteriorated.
|
|
|
When the engine starts, the engine-ECU calculates the internal resistance of the battery
by using the signal from the battery current sensor and the battery voltage. When the internal resistance
of the battery is more than the specified value, the judgement of the deteriorated battery decides
that battery is deteriorated.
|